The browser you are using is not supported. Please consider using a modern browser.
Connecticut’s Energy Usage and Energy Sources
In this post, we are going to take you through some of the main aspects of Connecticut’s energy consumption. Most of the data was gathered from the U.S. Energy Information Administration. But since that data can be hard to go through, we are presenting it in this easy to read format. Enjoy!
Major Takeaways
- Connecticut’s total energy consumption is 36th in all of the US but drops down to 46th when population is taken into account (2017)
- Connecticut’s top three energy sources were natural gas, nuclear, and motor gasoline (2017)
- Connecticut’s top three electricity sources were nuclear, natural gas, and biomass (2017)
- Nuclear and natural gas make up over 90% of Connecticut’s electricity consumption (2017)
- Renewable energy makes up about 5% of Connecticut’s electricity consumption. (2017)
Total Connecticut Energy Consumption
It is important to note that total energy consumption means all forms of energy, not only consumption through electricity but also consumption through things like cars and planes.
Connecticut used an estimated 726.4 trillion BTUs in 2017. This makes them 36th in the US for total energy consumption. However, when population is taken into account, they drop to 46th place with 203 million BTUs per capita.
The U.S. Energy Administration splits this usage into four categories.
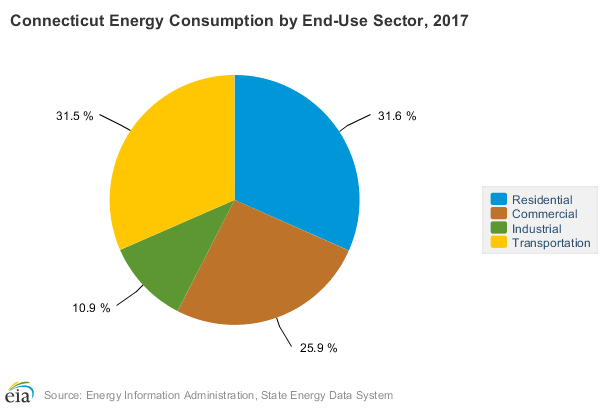
What Are Connecticut’s Energy Sources
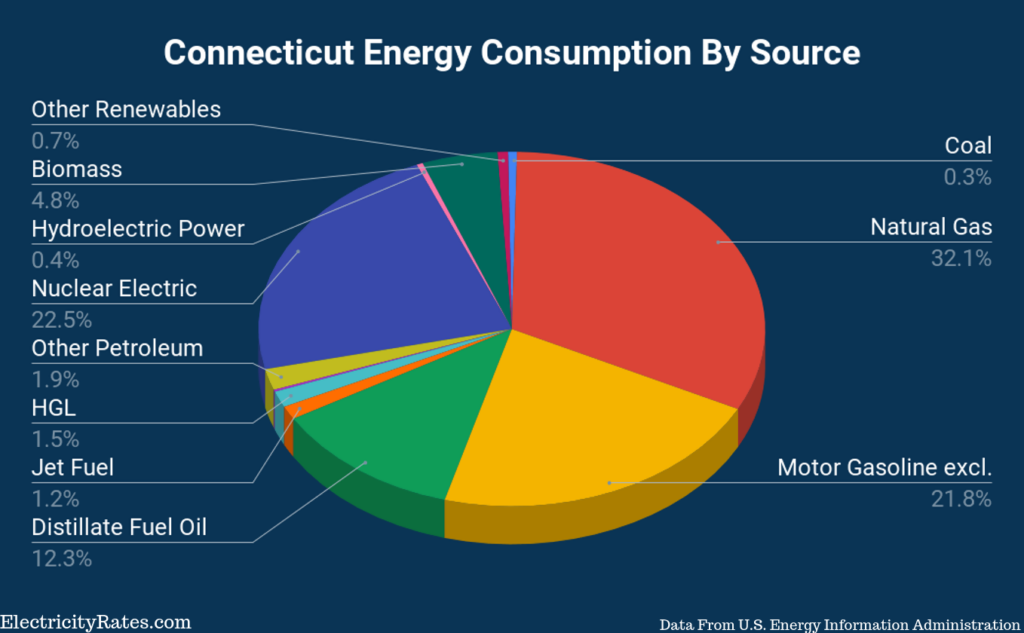
It is
important to note that 40.3 trillion BTUs traveled outside of state lines. The
total BTUs used by Connecticutcited above (726.4 trillion BTUs) does not
include this energy. The above percentages are based on the total 766.7
trillion BTUs. (2017)
Connecticut’s top three energy sources were:
- Natural Gas: 246.3 trillion BTUs
- Nuclear: 172.6 trillion BTUs
- Motor Gasoline: 167.3 trillion BTUs
Out of the total energy consumed by Connecticut in 2017, 246.3 trillion BTUs were from natural gas. According to the EIA, Connecticut does not have any fossil fuel reserves, so most of the natural gas that the state uses is shipped from Pennsylvania.
The second highest energy source is nuclear
energy at 172.6 trillion BTUs. All of this is provided by the Millston Power
Station, the state’s only nuclear power plant. Although nuclear energy does not
fall under the “renewable fuel” category, it is still carbon-free, meaning it
does not contribute to climate change.
Lastly, 167.3 trillion BTUs of motor gasoline
puts it in third place. With transportation taking up making up over 30% of the
state’s energy consumption, this is not very surprising.
45.2 trillion BTUs of renewable energy are used in
Connecticut, with biomass making up a little over 80% of it. Solar and
hydroelectric power make up the large majority of the rest.
What Generates Connecticut’s Electricity?
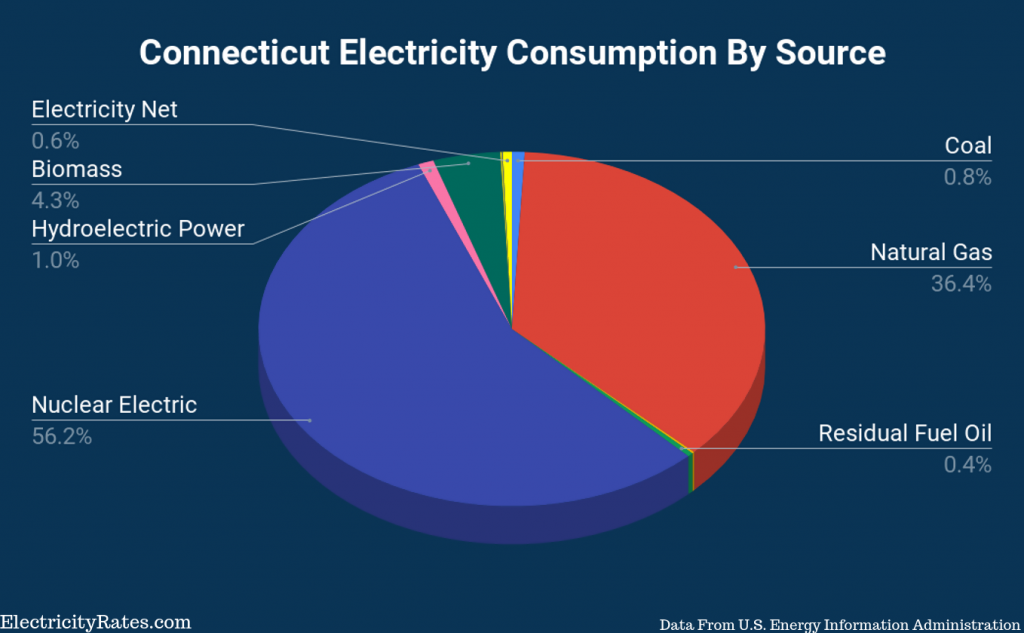
The top three energy sources for electricity were:
- Nuclear: 172.6 trillion BTUs
- Natural Gas: 111.7 trillion BTUs
- Biomass: 13.1 trillion BTUs
Out of the total energy Connecticut consumed,
306.8 trillion BTUs were consumed by the electric power sector.
172.6 trillion BTUs of nuclear were used in
electricity production in Connecticut, making up just over half of
Connecticut’s electricity production.
111.7 trillion BTUs of natural gas used toward
electricity puts it in second place for electricity production. Natural gas
also heats 35.2% of the homes in Connecticut and is likely why it is in first
place in regard to the total energy consumed.
In a distant 3rd place, we have Biomass at 13.1
trillion BTUs, which pretty much makes up the rest of the electricity
production and makes it the primary renewable resource used in Connecticut.
Other renewables include hydroelectric, solar, and wind at 3.1, 0.4, and 0.1
trillion BTUs respectively. All in all, renewables make up just over 5% of
electricity production in Connecticut.
[rates_search]